Optimal Average Household Pumping Schedule: Expert Tips & Guide
Understanding the Average Household Pumping Schedule
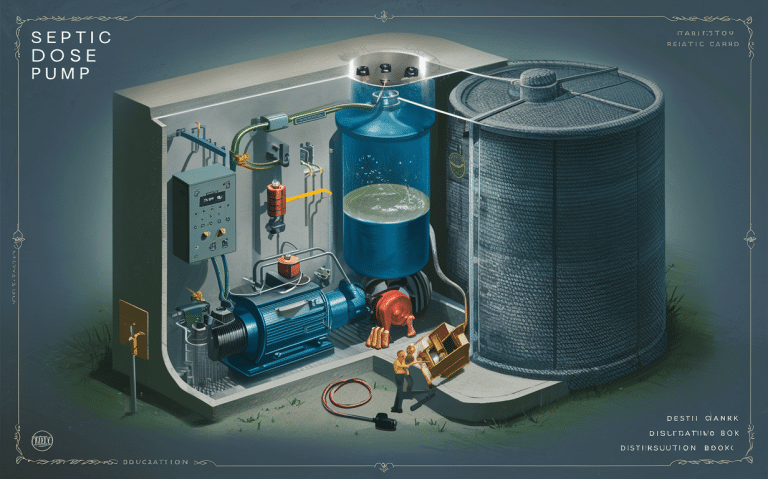
For most households, a typical septic system should be pumped every 3 to 5 years. This interval can vary based on several factors, including household size, water usage, and the size of the septic tank.
Consistent maintenance ensures the longevity and efficiency of your septic system, preventing costly repairs and environmental hazards.
Key Takeaways
- Regular pumping every 3-5 years is recommended for most households.
- Household size, water usage, and septic tank size are critical factors in determining the pumping schedule.
- Preventative maintenance can save money and avoid environmental damage.
Factors Influencing Your Pumping Schedule
Household Size
The number of people living in your home directly impacts how often you should pump your septic tank. More residents mean more water usage, leading to quicker tank fill-up.
For example, a family of four will produce more wastewater than a couple, necessitating more frequent pumping.
Water Usage
Daily activities like laundry, dishwashing, and showering contribute to the total volume of wastewater generated. High water usage accelerates the need for septic pumping.
Consider installing water-saving fixtures to reduce the burden on your septic system and prolong the intervals between pumpings.
Size of the Septic Tank
Septic tanks come in various sizes, typically ranging from 1,000 to 2,000 gallons for residential properties. A larger tank can hold more waste, allowing longer intervals between pumpings. However, even large tanks require regular maintenance to ensure efficiency.
Why Regular Pumping Is Essential
Preventing System Failures
Neglecting regular pumping can lead to septic system failures, causing backups and contamination of the surrounding environment. Regular pumping removes the accumulated sludge and scum, ensuring the system functions correctly.
Cost-Effectiveness
Preventative maintenance is cost-effective in the long run. The expense of regular pumping is minimal compared to the cost of repairing or replacing a failed septic system.
A Simple Guide to Estimating Your Pumping Schedule
| Household Size | Water Usage Level | Septic Tank Size (gallons) | Recommended Pumping Interval |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 people | Low | 1,000-1,200 | Every 5 years |
| 4 people | Medium | 1,200-1,500 | Every 3-4 years |
| 6 people | High | 1,500-2,000 | Every 2-3 years |
Signs That Indicate You Need to Pump Your Septic Tank
- Slow draining sinks and toilets: This is often the first sign of a full tank.
- Foul odors: Unpleasant smells around your septic tank or drain field could indicate a problem.
- Pooling water: Water pooling around your septic system is a clear sign of overflow.
- Sewage backups: This is a severe issue that requires immediate attention.
Tips for Maintaining Your Septic System
- Reduce water usage: Install water-saving devices and fix leaks promptly.
- Dispose of waste properly: Only flush biodegradable waste. Avoid flushing items like diapers, sanitary products, and grease.
- Regular inspections: Schedule periodic inspections to catch potential issues early.
- Keep records: Maintain a log of pumping dates and inspections.
Common Myths About Septic Pumping
Myth 1: Additives Eliminate the Need for Pumping
While some products claim to reduce the need for pumping, they are not a substitute for regular maintenance. Additives can help break down waste but won’t remove the sludge and scum that accumulate over time.
Myth 2: If It’s Not Broken, Don’t Fix It
Waiting until you notice a problem can lead to expensive repairs. Regular maintenance is essential to keep your system running smoothly.
The Role of Septic Inspections
Routine inspections can identify issues before they become severe. A qualified inspector will check the tank, leach field, and other components to ensure everything is functioning correctly.
Understanding the Components of a Septic System
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Septic Tank | Holds wastewater, allowing solids to settle and decompose |
| Leach Field | Distributes effluent into the soil for further treatment |
| Distribution Box | Evenly distributes wastewater to the leach field |
| Baffles | Prevents solids from leaving the tank and entering the leach field |
How Technology Is Changing Septic Maintenance
Modern technology, like remote monitoring systems and advanced filtration, makes it easier to maintain septic systems. These innovations provide real-time data and alerts, allowing for proactive management.
- Remote monitoring systems use sensors and wireless technology to continuously track the performance of septic systems. They can monitor factors like tank levels, pump performance, and potential leaks. This data is transmitted to a central monitoring station or mobile app, allowing homeowners and service providers to receive alerts and take action before issues arise.
- Advanced filtration technologies, such as aerobic treatment units (ATUs) and membrane bioreactors (MBRs), provide enhanced wastewater treatment capabilities. These systems use biological processes and advanced filters to remove contaminants more effectively than traditional septic systems, resulting in higher-quality effluent that can be safely discharged or reused.
- Other technological advancements include:
- Automated control systems that optimize septic system operations based on usage patterns and environmental conditions.
- Computerized maintenance tracking software that helps schedule timely inspections and service visits.
- Advanced septic tank designs with multiple chambers and improved baffling for better solids separation and retention.
By leveraging these technologies, homeowners and service providers can proactively monitor and maintain septic systems, reducing the risk of system failures, environmental contamination, and costly repairs.
Environmental Impact of Neglected Septic Systems
Failing septic systems can contaminate groundwater, posing serious health risks and damaging the environment. Regular pumping and maintenance protect local ecosystems and water sources.
Implementing a Maintenance Plan
Creating a maintenance plan tailored to your household’s needs ensures the longevity of your septic system. Include regular pumping, inspections, and water usage management in your plan.
- According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), the average household uses about 300 gallons of water per day (gpd) (Source). For septic systems, the EPA recommends pumping out the tank every 3 to 5 years (Source).
- The American Ground Water Trust reports that the average household well pumps every 6 to 12 months, depending on the water usage and the size of the well tank (Source).
- The National Ground Water Association suggests that well water systems be inspected and serviced annually, including pumping if necessary (Source).
Conclusion
Understanding and adhering to the average household pumping schedule is crucial for maintaining a healthy septic system. Regular pumping, mindful water usage, and routine inspections will keep your system functioning efficiently and prevent costly repairs.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure your septic system serves your household reliably for years to come.
Get your FREE estimates today, contact us!