Understanding Aerobic vs Anaerobic Systems Whats Best for Your Home
Understanding Aerobic vs Anaerobic Systems Whats Best for Your Home can significantly impact your home’s waste management efficiency. This comprehensive guide explores the difference between aerobic and anaerobic septic systems to help you make an informed decision for your property.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Aerobic systems utilize oxygen-dependent bacteria and mechanical aeration for faster waste breakdown
- Anaerobic septic systems rely on bacteria that thrive without oxygen, requiring less maintenance but slower processing
- System selection depends on property size, budget, local regulations, and soil conditions
- Both systems require different maintenance schedules and investment levels
- Local climate and usage patterns influence system performance
Understanding Aerobic vs Anaerobic Systems Whats Best for Your Home
Understanding Aerobic vs Anaerobic Systems Whats Best for Your Home is essential for homeowners considering wastewater treatment options. Both systems serve the primary purpose of breaking down household waste, but they do so through distinct processes that significantly impact their efficiency, maintenance requirements, and environmental effects.
Understanding Aerobic Septic Systems

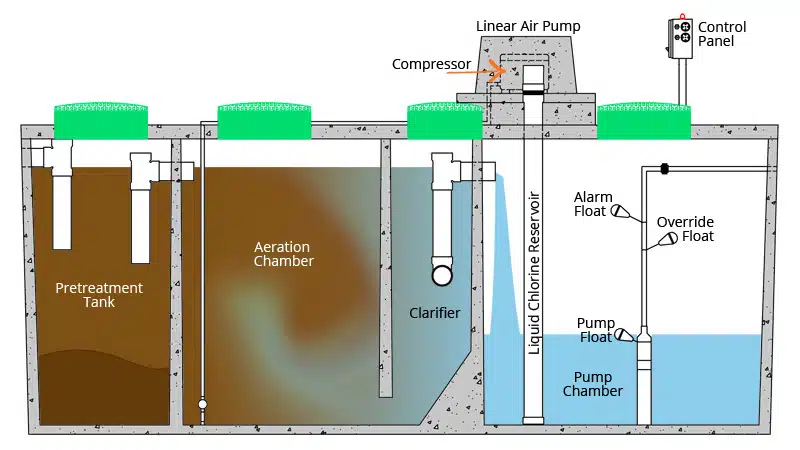
Aerobic septic systems represent the more technologically advanced option in residential waste management. These systems actively introduce oxygen to speed up waste decomposition.
How Aerobic Systems Work
- Wastewater enters the pretreatment tank
- Mechanical aerators inject oxygen into the treatment chamber
- Aerobic bacteria break down waste materials
- Treated effluent moves to the final treatment stage
- Cleaned water disperses into the drain field
Advantages of Aerobic Systems
- 40-60% faster waste processing than anaerobic systems
- Smaller footprint requirements
- Higher quality effluent
- Better for environmentally sensitive areas
- Reduced odor emissions
Disadvantages of Aerobic Systems
- Higher initial investment (10,000-30,000 dollars)
- Regular maintenance requirements
- Dependent on electrical power
- More complex mechanical components
- Higher operating costs
Understanding Anaerobic Septic Systems
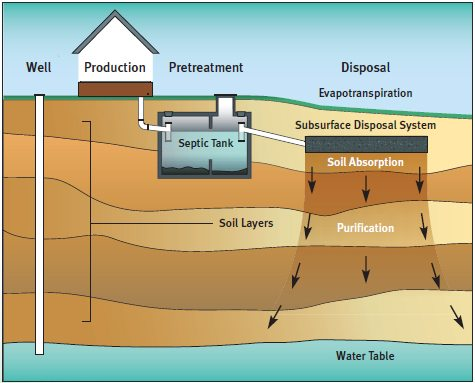
Traditional anaerobic septic systems, which operate without oxygen input, have been the standard in residential waste management for decades.
How Anaerobic Systems Work
- Wastewater flows into the main tank
- Solid waste settles at the bottom
- Anaerobic bacteria digest the waste
- Liquid effluent moves to the drain field
- Natural filtration occurs in the soil
Advantages of Anaerobic Systems
- Lower installation costs (3,000-10,000 dollars)
- No electricity required
- Simpler design with fewer components
- Less frequent maintenance is needed
- Proven long-term reliability
Disadvantages of Anaerobic Systems
- Slower waste processing
- Larger drain field requirements
- More noticeable odor potential
- Less effective in poor soil conditions
- Limited treatment capacity
Comparison Table: Aerobic vs. Anaerobic Systems
| Feature | Aerobic Systems | Anaerobic Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen Requirement | Requires oxygen | No oxygen needed |
| Treatment Speed | Fast | Slow |
| Maintenance Frequency | Regular monitoring | Less frequent |
| Initial Cost | Higher | Lower |
Factors Influencing System Selection
Consider these crucial elements when choosing between an aerobic versus anaerobic septic system:
Property Considerations
- Available space
- Soil type and composition
- Groundwater level
- Topography
- Climate conditions
Financial Factors
- Initial budget
- Long-term operating costs
- Maintenance expenses
- Expected system lifespan
- Property value impact
Regulatory Requirements
- Local health department regulations
- Environmental protection standards
- Permit requirements
- Inspection schedules
- Testing requirements
Maintenance Requirements
Aerobic System Maintenance
- Monthly system checks
- Quarterly filter cleaning
- Annual professional inspection
- Regular pump-out (2-3 years)
- Mechanical component testing
Anaerobic System Maintenance
- Annual inspection
- Pump-out every 3-5 years
- Drain field monitoring
- Waste level checking
- Water usage management
Expert Tips for System Success
- Monitor water usage patterns
- Follow maintenance schedules
- Use septic-safe products
- Keep accurate maintenance records
- Address issues promptly
Frequently Asked Questions
Which system is better for the environment?
Aerobic systems generally produce cleaner effluent but consume more energy. The environmental impact depends on your specific situation and priorities.
How often should systems be inspected?
Aerobic systems need monthly checks and quarterly professional inspections. Anaerobic systems require annual professional inspections.
Can I switch from one system to another?
Yes, but conversion requires significant excavation and investment. Consult with a professional to evaluate feasibility.
Conclusion
The choice between aerobic and anaerobic septic systems depends on your needs, property characteristics, and budget. While aerobic systems offer faster treatment and better efficiency, anaerobic systems provide reliability with lower maintenance requirements. Consider all factors carefully and consult with local experts before making your decision.
For professional guidance on septic system selection and maintenance in Middletown, New York, contact United Sewer & Septic. Our experienced team can help you make the best choice for your property septic system, contact United Sewer & Septic. Our team in Middletown, New York, is ready to help you.



